D-limonene is a natural active ingredient of plant origin used in veterinary medicine mainly in dogs and cats against some external parasites (lice, fleas, flies, etc). It is also used against agricultural and household pests.
Common name: D-LIMONENE
Type: INSECTICIDE, REPELLENT
Some plants where it is found
- Anethum graveolens (dill)
- Carum carvi (Caraway, Persian cumin)
- Citrus spp (citrus fruits: oranges, lemons, etc.)
- Coriandrum sativum (coriander, cilantro, Chinese parsley)
- etc.
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
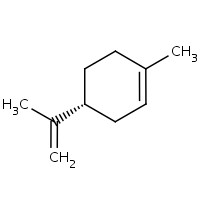
EFFICACY AGAINST PARASITES
Type of action: Insecticide, Repellent
Main veterinary parasites controlled: fleas, lice, mosquitoes, etc.
Mechanism of action: Little is known about the molecular mechanism of action of d-limonene. It is thought to be neurotoxic and to act upon sensory cells increasing their activity. Such cells send wrong signals to the muscles causing tremors, convulsions and loss of coordination. It seems that it can also affect the central nervous system leading to hyperstimulation of motor neurons. All this can quickly cause paralysis of the affected insects. However, they can recover quite quickly unless d-limonene is administered together with PBO (piperonyl butoxide), a synergist that potentiates its efficacy. A certain repellent effect has also been reported for D-limonene.
However, a "crushing" efficacy should not be expected from natural products, comparable to that of modern synthetic insecticides, which are more potent and persistent than any natural compound. Simplifying, it can be said that natural active ingredients can be useful in places or seasons with low parasite challenge, but may be insufficient for controlling well established parasite populations (fleas, ticks, mites, etc.) in pets, let alone in livestock.
Efficacy against a specific parasite depends on the delivery form and on the dose administered. Check the labels of the products available in your country.
Click here for general information on features and characteristics of PARASITICIDES.
SAFETY
Oral LD50, rat, acute*: 4400-5100 mg/kg (male, female)
Dermal LD50, rat, acute*: >5000 mg/kg
* These values refer to the active ingredient. Toxicity has to be determined for each formulation as well. Formulations are usually significantly less toxic than the active ingredients.
Used in sprays or baths at 5-10x the recommended concentration d-limonene can cause toxic symptoms such as hypersalivation (drooling), muscular tremors, ataxia (lack of coordination) and severe hypothermia (low temperature).
D-limonene and its oxidation products are a moderate skin, eye and mucosal irritants. D-limonene in the air can be sensitizing and cause allergies. Otherwise D-limonene is considered as rather safe for humans, domestic animals and the environment.
It must be remembered that the natural origin does not guarantee that such compounds are less toxic than the synthetic parasiticides. They are as "chemical" as the synthetic ones. Toxicity is a matter of dose!
General information on the safety of veterinary antiparasitics is available in specific articles in this site (click to visit):
- General safety of antiparasitics for domestic animals
- General safety of antiparasitics for humans
- General safety of antiparasitics for the environment
MARKETING & USAGE
D-limonene is produced mainly from essential oils of the peels of citrus fruits (>90% in orange peel oil, ~65% in lemon peel oil), which are secondary products in the citrus juice industry. Although industrial chemical synthesis wouldn't be complicated based on the rather simple molecular structure, the abundance of natural material allows low production costs.
Use in LIVESTOCK: Yes, very scarce
Use in HORSES: Yes, very scarce
Use in DOGS & CATS: Yes, moderate
Use in humans: Yes, mainly in cosmetics, and in traditional medicine
Use in public/domestic hygiene: Yes
Use in agriculture: Yes, moderately
PARASITE RESISTANCE
Reported in livestock & horses: NO
Reported in pets: NO
Reported in other uses: NO
Learn more about parasite resistance and how it develops.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION

D-limonene is one of the two optic isomers of limonene. Limonene is a natural cyclic terpene produced by many plants, particularly by citrus fruits (orange, lemon, mandarin, etc.). It has a characteristic orange smell. The l-isomer smells like terpentine and is more abundant in other plants (e.g. in pine needles and cones).
Use of d-limonene as an insecticide is very modest compared with other industrial uses as fragance in cosmetics, home and personal care products as well as in the food industry. It is also used as a biodegradable solvent, as well as in traditional medicine from various cultures.
D-limonene shares two features with many other natural insecticides and repellents: it is rather volatile and is unstable when exposed to sunlight. Consequently its effect in animals exposed to sunlight is very short: a few days or even only a few hours. This means that protection of the treated animals against re-infestations (residual effect) is virtually inexistent. This is particularly unfavorable for livestock that would need to be treated very frequently. However, for the same reason they do not leave chemical residues in food commodities (meat, milk, eggs, etc.), which is a benefit sought by organic producers.
Another disadvantage of many "natural products" extracted from plants is that quality (and thus efficacy) may vary, even if used following the label instructions, because producing extracts from heterogeneous plant materials is often less reliable than chemical synthesis.
Finally it must be said that in many countries registration of so-called "natural products" does not need a (serious) proof of efficacy, quality and safety as pesticides or veterinary medicines. This means that many such products have not been seriously tested in clinical trials in the field and consequently their efficacy and/or safety may not be granted. For such products, getting a market authorization does not need a substantial investment, which explains why there are so many brands in most countries.
- Click here to view the list of all technical summaries of natural antiparasitic active ingredients in this site.
- Click here to view the list of all technical summaries of antiparasitic active ingredients in this site.
- Click here to visit the article on medicinal plants with antiparasitic properties in this site.