Clorsulon is a narrow-spectrum antiparasitic active ingredient used in veterinary medicine. It is used in livestock against liver flukes. It is not used against agricultural and household pests. It belongs to the chemical class of the sulphonamides.
Common name: CLORSULON
Type: veterinary medecine
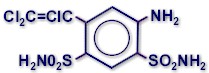
Chemical class: benzenesulphonamide
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
EFFICACY AGAINST PARASITES
Type of action: Flukicide anthelmintic, endoparasiticide
Main veterinary parasites controlled: Liver flukes
Efficacy against a specific parasite depends on the delivery form and on the dose administered.
Click here for general information on features and characteristics of PARASITICIDES.
DOSING
Closulon is a narrow-spectrum anthelmintic effective against some flukes (e.g. Fasciola hepatica). It is not effective against roundworms, tapeworms or external parasites.
It is used moderatly in ruminants mainly as an injectable and very little as a drench, mostly in mixture with ivermectin to add flukicidal activity.
The table below indicates some usual dosing recommendations for clorsulon issued by manufacturers or documented in the scientific literature. They may not be approved in some countries.
| Dosing recommendations for CLOSULON |
||
| CATTLE | ||
| Delivery | Parasites | Dose (against clorsulon-susceptible parasites) |
| Oral | Fasciola hepatica, Fasciola gigantica | 7 mg/kg |
| Oral | Fascioloides magna | 21 mg/kg |
| Subcutaneous | Fasciola hepatica | 2-8 mg/kg |
| SHEEP & GOATS | ||
| Oral | Fasciola hepatica | 7 mg/kg |
| Subcutaneous | Fasciola hepatica | 2-4 mg-kg |
| SOUTHAMERICAN CAMELIDS |
||
| Oral | Fasciola hepatica | 7 mg-kg |
DISCLAIMER: Liability is denied for any possible damage or harm to persons, animals or any other goods that could follow the transmission or use of the information, data or recommendations in this site by any site visitor or third parties.
Dosing recommendations for antiparasitics depend on national regulations. National regulatory authorities determine whether a product is approved for a given indication, i.e. use on a particular host at a specific dose and against a specific parasite. Check the labels of the products available in your country for specific information on approved indications.
SAFETY
Oral LD50, rat, acute*: >10'000 mg/kg
Dermal LD50, rat, acute*: not found
* These values refer to the active ingredient. Toxicity has to be determined for each formulation as well. Formulations are usually significantly less toxic than the active ingredients.
MRL (maximum residue limit) established for either beef, mutton pork or chicken meat*:
- CODEX: No
- EU: Yes
- USA: Yes
- AUS: Yes
* This information is an indicator of the acceptance of an active ingredient by the most influential regulatory bodies for use on livestock.
Withholding periods for meat, milk, eggs, etc. depend on delivery form, dose and national regulations. Check the product label in your country.
Learn more about clorsulon safety (poisoning, intoxication, overdose, antidote, symptoms, etc.).
General safety information for antiparasitics is available in specific articles in this site (click to visit):
- General safety of antiparasitics for domestic animals
- General safety of antiparasitics for humans
- General safety of antiparasitics for the environment
|
WARNING It is obvious that veterinary products are not intended for and should never be used on humans!!! |
MARKETING & USAGE
Decade of introduction: 1970
Introduced by: MS&D AGVET → MERIAL
Some original brands: CURATREM
Patent: Expired (particular formulations may be still patent-protected)
Use in LIVESTOCK: Yes, moderate in ruminants
Use in HORSES: NO
Use in DOGS and CATS: No
Main delivery forms:
Use in human medicine: No
Use in public/domestic hygiene: No
Use in agriculture: No
Generics available: Yes, a few
PARASITE RESISTANCE
In livestock: Yes, a few reports in liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) on sheep, but seems not to be a widespread problem.
Learn more about parasite resistance and how it develops.
SPECIFIC FEATURES
Clorsulon is a specific narrow-spectrum veteran flukicide, moderately used on livestock, mainly ruminants (cattle, sheep and goats). Nowadays it is almost only available in combination with ivermectin, mostly as an injectable but also as a drench.
It is not used on dogs and cats.
Efficacy of clorsulon
Clorsulon is highly effective against adults and late immature stages (>8 weeks) of the common liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica). It is also effective against Fasciola gigantica and Fascioloides magna, two other liver fluke species important for livestock.
It has no efficacy against roundworms, tapeworms or any external parasite.
Pharmacokinetics of clorsulon
Ingested clorsulon is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream. Maximum plasma levels are achieved 14 to 24 hours after administration. After subcutaneous injection maximum plasma levels are reached earlier, about 6 hours after treatment. Clorsulon binds strongly (~75%) to plasmatic proteins.
Excretion half-life after oral administration is about 26 hours. 45-50% of the administered dose is excreted unchanged through urine.
Goats have a higher capacity for metabolizing clorsulon than sheep: bioavailability of clorsulon in goats is only 60% of the bioavailability in sheep, which explains its lower efficacy in goats.
Mechanism of action of clorsulon
Clorsulon inhibits various enzymes involved in the glycolytic process of flukes, i.e. it makes it impossible for the flukes to obtain energy from glucose. As a consequence the levels of ATP, the cellular fuel, are depressed.
Click here to view the list of all technical summaries of antiparasitic active ingredients in this site.