Nitenpyram is an antiparasitic active ingredient used in veterinary medicine in dogs and cats against fleas. It is also used against agricultural pests. It belongs to the chemical class of the neonicotinoids.
Common name: NITENPYRAM
Type: pesticide
Chemical class: neonicotinoid
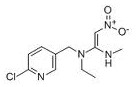
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
EFFICACY AGAINST PARASITES
Type of action: Contact, systemic insecticide
Main veterinary parasites controlled: fleas
Efficacy against a specific parasite depends on the delivery form and on the dose administered. National regulatory authorities determine whether a product is approved for a given indication, i.e. use on a particular host at a specific dose and against a specific parasite. Check the labels of the products available in your country.
Click here for general information on features and characteristics of PARASITICIDES.
DOSING
Nitenpyran is a systemic insecticide that belongs to the chemical class of the neonicotinoids. It is highly effective against fleas but not against ticks or mites, or any internal parasites.
A particular feature of nitenpyram is that it kills fleas very quickly after administration: >99% after only 4 hours. But it does not protect treated animals against re-infestation beyond 1-2 days. It is used in dogs and cats mainly in tablets for oral administration. So far it is not used in livestock or horses.
The table below indicates some usual dosing recommendations for nitenpyram issued by manufacturers or documented in the scientific literature. They may not be approved in some countries.
| Dosing recommendations for NITENPYRAM |
||
| Delivery | Parasites | Dose (against nitenpyram-susceptible parasites) |
| DOGS | ||
| Tablets | Fleas | 1-14 mg/kg, dep. on animal's weight |
| CATS | ||
| Tablets | Fleas | 1-5.2 mg/kg, dep. on animal's weight |
DISCLAIMER: Liability is denied for any possible damage or harm to persons, animals or any other goods that could follow the transmission or use of the information, data or recommendations in this site by any site visitor or third parties.
Dosing recommendations for antiparasitics depend on national regulations. National regulatory authorities determine whether a product is approved for a given indication, i.e. use on a particular host at a specific dose and against a specific parasite. Check the labels of the products available in your country for specific information on approved indications.
SAFETY
Oral LD50, rat, acute*: 1680 mg/kg
Dermal LD50, rat, acute*: >2000 mg/kg
* These values refer to the active ingredient. Toxicity has to be determined for each formulation as well. Formulations are usually significantly less toxic than the active ingredients.
MRL (maximum residue limit): Not applicable: not approved for livestock
Withholding periods for meat, milk, eggs: Not applicable: not approved for livestock
Recently (April 2013) the EU has prohibited for two years the use of several nicotinoids on various crops due to suspected detrimental effects on bee colonbies. This should have no influence on veterinary uses of neonicotinoids.
Learn more about nitenpyram safety.
General safety information for antiparasitics is available in specific articles in this site (click to visit):
- General safety of antiparasitics for domestic animals
- General safety of antiparasitics for humans
- General safety of antiparasitics for the environment
|
WARNING Never use agricultural or hygiene products with this or any other active ingredient on livestock or pets, even if there are veterinary products with this same active ingredient approved for use on animals. The formulations for agricultural or hygiene use are different and may be toxic for livestock or pets. It is obvious that veterinary products are not intended for and should never be used on humans!!! |
MARKETING & USAGE
Decade of introduction: 1990
Introduced by: TAKEDA and CIBA-GEIGY (→ NOVARTIS → ELANCO)
Some original brands: CAPSTAR, BESTGUARD
Patent: Expired (particular formulations may be still patent-protected)
Use in LIVESTOCK: No
Use in HORSES: NO
Use in DOGS and CATS: YES, scarce
Main delivery forms:
Use in human medicine: No
Use in public/domestic hygiene: No
Use in agriculture: Yes
Generics available: Yes, so far not for veterinary use
PARASITE RESISTANCE
In pets: No
Learn more about parasite resistance and how it develops.
SPECIFIC FEATURES
Nitenpyram is a neonicotinoid used on pets against fleas (CAPSTAR). It is only available in the form of Tablets for oral administration. It is not used in livestock or horses.
Efficacy of nitenpyram
Nitenpyram for veterinary use is only effective against fleas. It has no effect whatsoever against ticks, mites or lice. However, it is one of the fastest flea killers in the market. As soon as 4 hours after administration it already kills 99% of the fleas on a pet, whereas most other products need at least 24 hours. It is appreciated as an instant or emergency flea killer. However, it has no residual effect, i.e., protection against re-infestation does not last more than 24 hours.
Pharmacokinetics of nitenpyram
After oral administration nitenpyram is very quickly absorbed to blood. Effective concentration in blood plasma is reached as soon as 10 to 20 minutes after administration. It is also quickly eliminated, mainly through the kidneys. Excretion half-time in dogs is about 2-3 hours, in cats about 8-16 hours. 48 hours after administration is almost completely eliminated, about 40% in the form of unchanged nitenpyram, the rest in the form of various metabolites.
Mechanism of action of nitenpyram
As all neonicotinoids nitenpyram is an agonists of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It takes the place of the normal neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the receptors, which cannot be deactivated by acetylcholinesterase and remains irreversibly blocked. This leads to an over stimulation of the nerve cells, to paralysis and to death of the affected insect.
These receptors are found in the central and peripheral nervous system of mammals, but only in the central nervous systems of insects. Neonicotinoids bind much more strongly to insect receptors than to mammal receptors, which makes them relatively safe for domestic animals and humans.
Click here to view the list of all technical summaries of antiparasitic active ingredients in this site.