Citronellal is a natural active ingredient of plant origin used in veterinary medicine mainly in dogs and cats against some external parasites (lice, fleas, flies, etc). It is also used against agricultural and household pests.
Common name: CITRONELLAL
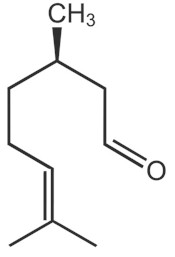
Other names: rhodinal or 3,7-dimethyloct-6-en-1-al
Type: INSECTICIDE, REPELLENT
Some plants where it is found
- Citrus spp (orange, lemon, mandarine, etc), particularly in Citrus hystrix (kaffir lime)
- Corymbia citriodora (lemon-scented gum)
- Cymbopogon citratus (lemon grass) etc.
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
EFFICACY AGAINST PARASITES
Type of action: Repellent
Main veterinary parasites controlled: mosquitoes, flies, etc.
Mechanism of action: It has been reported that citronellal directly activates calcium channels in the neurons of several mosquito species in a similar way as the overexciting and repellent effect of pyrethrins. In Drosophila melanogaster flies citronellal is detected by protein receptors known as TRP (Transient Receptor Potential) channels. Once activated these receptors send signals to the insect brain that cause an aversive response.
However, a "crushing" efficacy should not be expected from natural products, comparable to that of modern synthetic insecticides, which are more potent and persistent than any natural compound. Simplifying, it can be said that natural active ingredients can be useful in places or seasons with low parasite challenge, but may be insufficient for controlling well established parasite populations (fleas, ticks, mites, etc.) in pets, let alone in livestock.
Efficacy against a specific parasite depends on the delivery form and on the dose administered. Check the labels of the products available in your country.
Click here for general information on features and characteristics of PARASITICIDES.
SAFETY
Oral LD50, rat, acute*: 2420 mg/kg
Dermal LD50, rat, acute*: >2500 mg/kg
* These values refer to the active ingredient. Toxicity has to be determined for each formulation as well. Formulations are usually significantly less toxic than the active ingredients.
Citronellal is a light skin irritant and can occasionally cause allergies. Otherwise it is considered as rather safe for use on humans and domestic animals.
It must be remembered that the natural origin does not guarantee that such compounds are less toxic than the synthetic parasiticides. They are as "chemical" as the synthetic ones. Toxicity is a matter of dose!
General information on the safety of veterinary antiparasitics is available in specific articles in this site (click to visit):
- General safety of antiparasitics for domestic animals
- General safety of antiparasitics for humans
- General safety of antiparasitics for the environment
MARKETING & USAGE
Citronellal is the major component (≤80%) in the essential oil of Citrus hystrix (kaffir lime) and to a lesser extent in oils of other plants. Today it can be manufactured through industrial extraction of citronella oil, but also through various synthetic processes.
Use in LIVESTOCK: Yes, extremely scarce
Use in HORSES: Yes, very scarce
Use in DOGS & CATS: Yes, scarce
Use in human medicine: Yes, in a few repellents (mosquitoes, head lice)
Use in public/domestic hygiene: Yes, scarce
Use in agriculture: Yes, scarce
PARASITE RESISTANCE
Reported in livestock & horses: NO
Reported in pets: NO
Reported in other uses: NO
Learn more about parasite resistance and how it develops.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION

Citronellal is a monotrpenoid naturally produced by several plants. It is the major constituent (≥80%) in the essential oil of Citrus hystrix (kaffir lime). It has a distinctive lemon scent that makes it very useful in the cosmetic, perfume and personal care industry to create numerous fragrances. Citronellal is also used as a precursor in the industrial production of menthol and as an aromatic additive in the tobacco industry. It has also antifungal properties.
The use of citronellal as a repellent is rather modest when compared with its industrial uses. It can be found in a few more or less "ecological" products against various pests in horticulture, against some domestic pests, and against a few veterinary parasites (mosquitoes, flies, ticks, etc.). But often the essential oils that contain citronellal are used, not directly citronellal.
Citronellol is the alcohol of citronellal, and has similar properties. It is also used in cosmetic and personal care products.
Citronellal shares two features with many other natural insecticides and repellents: it is rather volatile and is unstable when exposed to sunlight. Consequently its effect in animals exposed to sunlight is very short: a few days or even only a few hours. This means that protection of the treated animals against re-infestations (residual effect) is virtually inexistent. This is particularly unfavorable for livestock that would need to be treated very frequently. However, for the same reason they do not leave chemical residues in food commodities (meat, milk, eggs, etc.), which is a benefit sought by organic producers.
Another disadvantage of many "natural products" extracted from plants is that quality (and thus efficacy) may vary, even if used following the label instructions, because producing extracts from heterogeneous plant materials is often less reliable than chemical synthesis.
Finally it must be said that in many countries registration of so-called "natural products" does not need a (serious) proof of efficacy, quality and safety as pesticides or veterinary medicines. This means that many such products have not been seriously tested in clinical trials in the field and consequently their efficacy and/or safety may not be granted. For such products, getting a market authorization does not need a substantial investment, which explains why there are so many brands in most countries.
- Click here to view the list of all technical summaries of natural antiparasitic active ingredients in this site.
- Click here to view the list of all technical summaries of antiparasitic active ingredients in this site.
- Click here to visit the article on medicinal plants with antiparasitic properties in this site.